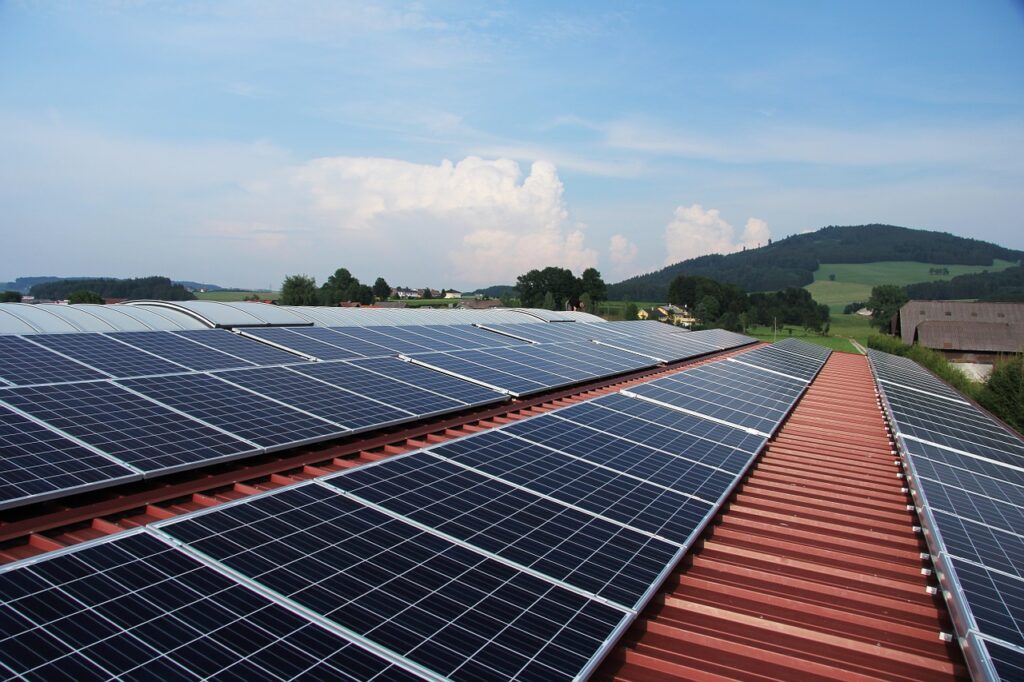
Photovoltaics is a hot topic lately. Much is being said about it, even more is being written. Encouraging promotions, subsidies or allowances are appearing. We are seeing more and more of these 'strange rectangles' on houses.
But what is photovoltaics really and what principle does it work on? You will find the answer to these questions in the following post. I encourage you to read it!
WHAT IS SOLAR ENERGY?
Solar energy is radiant energy emitted by the sun. In order to reduce fuel consumption and minimise the so-called carbon footprint, i.e. the sum of greenhouse gas emissions, it is worth using solar energy to meet the constantly growing demand for electricity. The easiest option is to install a photovoltaic system that converts solar radiation into electricity.
WHAT IS PHOTOVOLTAICS?
The word PHOTOWOLTAIKA comes from the two words 'FOTO', meaning light, and 'VOLTAIKA', meaning electricity. The solar cell (photovoltaic cell) is the main component of the entire technology. Photovoltaic systems use their properties to convert solar energy into electricity. These cells consist of one or two layers of semiconductor, with silicon being the most commonly used material. The cells connected together form a photovoltaic module (panel) and all the panels form a DC generator.
HOW DO CELLS GENERATE ELECTRICITY FROM LIGHT?
When sunlight illuminates the panel an electric field is generated across the layers, causing direct current (DC) to flow. The more intense the light, the greater the current flow. However, it is important to remember that the modules produce direct current, so this energy must be converted into alternating current (AC), which flows in our sockets and can be used for our needs or given to a power station for storage. The device that converts direct current into alternating current is called an inverter or inverter.
THERE ARE 3 BASIC TYPES OF PHOTOVOLTAIC PANELS
MONOCRYSTALLINE
Monocrystalline cells are cut from a single silicon crystal and are the most efficient type of cell, but are not the most popular due to their higher price. In addition to increased efficiency, they are more aesthetically pleasing - characterised by their deep black colour.
POLYCRYSTALLINE
These modules are made from a block of silicon that consists of multiple crystals. They are slightly less efficient but cheaper than monocrystalline, which is why they are very popular. A small plus point is the minimally lower temperature coefficient, which means that as the temperature increases, the power drops less with polycrystalline cells than with monocrystalline cells.
AMORPHIC
This type of cell is made by placing a thin layer of non-crystalline silicon on a wide range of surfaces. It is the cheapest and least efficient type of panel. It can be flexible yet resistant to mechanical damage.
WHAT ARE THE MAIN BENEFITS OF A PHOTOVOLTAIC INSTALLATION?
LOWER ELECTRICITY BILLS
Current installations can cover 100% of your electricity needs. Your annual electricity bill will be a maximum of £200 and these will be fixed charges only. You will no longer have to stress about rising electricity prices.
LOWER CO2
A typical 2.5 kWp installation can meet 50% of domestic electricity demand, saving around 1,200kg of CO2 per year and around 30 tonnes over its lifetime.