Photovoltaic mounting systems for a flat roof - what options do builders have?
Photovoltaic mounting systems for flat roofs are designed to maximise the performance of the solar panels while ensuring their stability and safety. A variety of technologies and methods are used to install panels on flat roofs, which must take into account factors such as the direction, pitch of the panels, wind and snow loads, as well as the integrity of the roof structure itself. The following are possible technical solutions for the most common flat roof covering - i.e. felt or membrane covering:
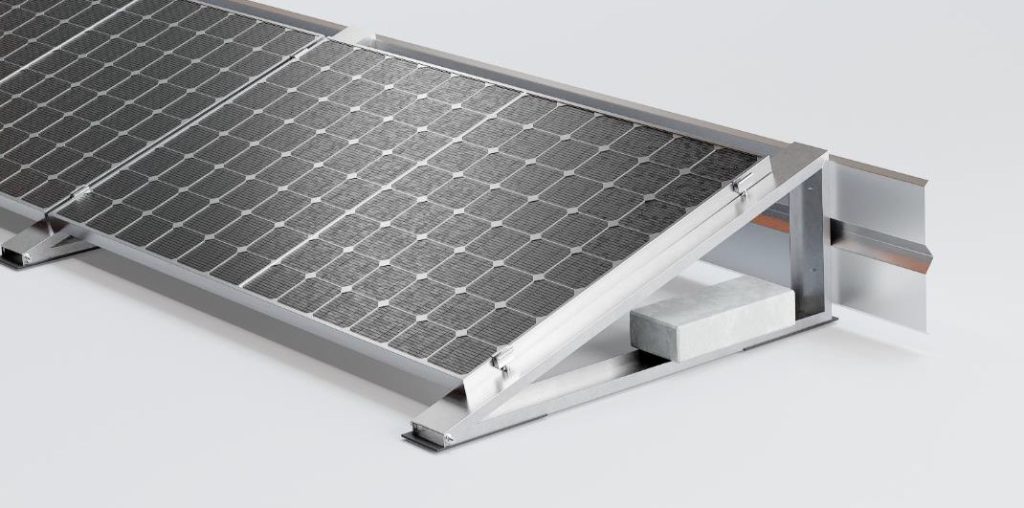
- Ballast systems: These are systems that use weight (known as ballast, such as concrete slabs or blocks) to stabilise the mounting structure of photovoltaic panels without penetrating the roof. They are popular because of the simplicity of installation and the minimal risk of roof damage. However, such installation is not possible on every roof due to limitations in the allowable roof load.
Figure 1 Ballast system with windlass
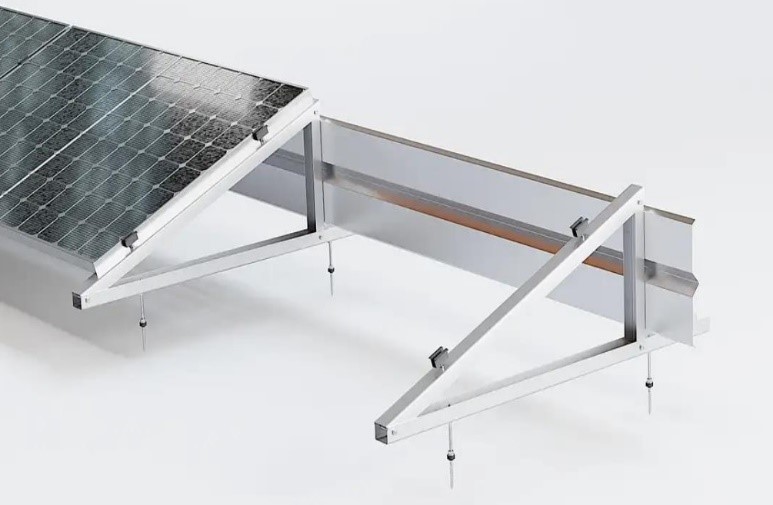
- Systems with anchoring: They require mechanical fixing to the roof structure, which provides greater stability, but involves penetration of the roof surface. This makes these systems more resistant to strong winds. However, such an installation is not possible with a membrane-covered roof or when there is an insulation layer under the roofing felt, such as polystyrene.
Figure 2 Anchored system with windlass
- Bonded systems: This is a solution in which special fixing plates are welded between the existing and newly laid roofing felt or membrane. This system avoids the disadvantages of the two previously mentioned systems - no ballast is used, so the load on the roof is considerably lower, and there is no penetration of the roof insulation layers (method with anchoring). The disadvantage of the glued system is the time-consuming installation and therefore its price.
Figure 3 Bonded system with windlass
All mounting systems should be certified and tested by the manufacturers. It is recommended that the entire mounting system comes from a single manufacturer/supplier in order to maintain the highest possible degree of safety.
Among the factors to consider when selecting the optimal design is the direction of panel alignment. You can choose a system in which all the panels face south or one in which the panels are arranged in an east-west orientation. A south-facing photovoltaic installation will have a higher total annual electricity production. An east-west installation, on the other hand, will enable greater use of roof space and also allow for increased self-consumption.
Regardless of the method chosen for fixing the panels to the roof, it is advisable in all cases, especially in areas with strong winds or on taller buildings, to use so-called wind girders. These are specially shaped and selected elements that protect the panels from the wind. This is an additional cost, but well worth it due to the significant increase in the safety of the installation.
Choosing the right mounting system depends on a number of factors, including the specifics of the roof, local weather conditions, budget and performance targets for the photovoltaic system. It is important to consult with a specialist before making a decision to help assess the best option for your property. Feel free to contact our representatives to select the optimal solution for you.